XBeam2D XFrame2D Eurocode Steel: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "thumb '''EN 1993-1-1 / EN 1995-1-1''' Specifically and only for the check according to Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 respectively Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 data can be inserted. '''Beam group''' Specifically and only for the lateral-torsional buckling resistance check a beam group can be inserted here. XFrame2d automatically detects for which beams this qualifies. Only the beams which are connected by a fully fixed connection to thi...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:XBeam2DEurocode.png| | [[File:XBeam2DEurocode.png|675x675px]] | ||
'''EN 1993-1-1 / EN 1995-1-1''' | '''EN 1993-1-1 / EN 1995-1-1''' | ||
Specifically and only for the check according to Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 respectively Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 data can be inserted. | Specifically and only for the check according to Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 respectively Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 data can be inserted. | ||
'''Beam group''' | '''Beam group''' | ||
Specifically and only for the lateral-torsional buckling resistance check a beam group can be inserted here. XFrame2d automatically detects for which beams this qualifies. Only the beams which are connected by a fully fixed connection to this particular beam and have the same profile will be | Specifically and only for the lateral-torsional buckling resistance check a beam group can be inserted here. XFrame2d automatically detects for which beams this qualifies. Only the beams which are connected by a fully fixed connection to this particular beam and have the same profile will be shown. You can select which beams should be taken into account. For this group you subsequently enter the length between the lateral restraints and the buckling length out of plane. | ||
'''Cantilever''' | |||
'''Cantilever''' | '''Cantilever''' | ||
Setting if the beam should be considered as a cantilever. | Setting if the beam should be considered as a cantilever. | ||
'''Lateral torsional buckling''' | '''Lateral torsional buckling''' | ||
| Line 22: | Line 18: | ||
Amount of lateral supports / distances between lateral supports | Amount of lateral supports / distances between lateral supports | ||
This is only relevant for the check of lateral torsional buckling. You can enter the lateral supports for the top and the bottom flange. | This is only relevant for the check of lateral torsional buckling. You can enter the lateral supports for the top and the bottom flange. | ||
'''There are 3 possibilities:''' | |||
'''There are 3 possibilities:''' | '''There are 3 possibilities:''' | ||
1. Number: The amount of lateral supports. | 1. Number: The amount of lateral supports. They are the extra (lateral supports) between the supports distributed over the length of the beam(group) | ||
2. Distances: The lengths between the lateral restraints from the beginning of the beam (group). The syntax is ''length1 length2 amountxlenght3.. etc''. | 2. Distances: The lengths between the lateral restraints from the beginning of the beam (group). The syntax is ''length1 length2 amountxlenght3.. etc''. | ||
For example 3000 3x2200 2800 | For example 3000 3x2200 2800 | ||
3. Node numbers Selecting the node numbers which are in the beam group. | 3. Node numbers Selecting the node numbers which are in the beam group. | ||
'''Buckling length''' | |||
'''Buckling length''' | '''Buckling length''' | ||
The buckling length out of plane. According to the check by Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 resp. Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 this is based on a geometric non linear force distribution. This means that the buckling of the beams in the plane of the frameworks is provided | The buckling length out of plane. According to the check by Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 resp. Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 this is based on a geometric non linear force distribution. This means that the buckling of the beams in the plane of the frameworks is provided implicitly. For every load combination the internal stability is determined iteratively. | ||
However buckling out of the plane should be reviewed. Default the buckling lengths out of plane are taken equal to the beam length. In case this does not hold a different buckling length can be entered. | However buckling out of the plane should be reviewed. Default the buckling lengths out of plane are taken equal to the beam length. In case this does not hold a different buckling length can be entered. | ||
'''Check deflection''' | '''Check deflection''' | ||
Setting if deflection has to be checked. | Setting if deflection has to be checked. | ||
'''Type''' | '''Type''' | ||
This influences the requirement of additional deflection. | This influences the requirement of additional deflection. | ||
'''Additional deflection''' | '''Additional deflection''' | ||
Requirement of additional deflection. | Requirement of additional deflection. | ||
'''Final deflection''' | '''Final deflection''' | ||
Requirements of final deflection. | Requirements of final deflection. | ||
'''Pre-camber''' | '''Pre-camber''' | ||
The size of pre-camber in mm. | The size of pre-camber in mm. | ||
Latest revision as of 21:23, 11 November 2022
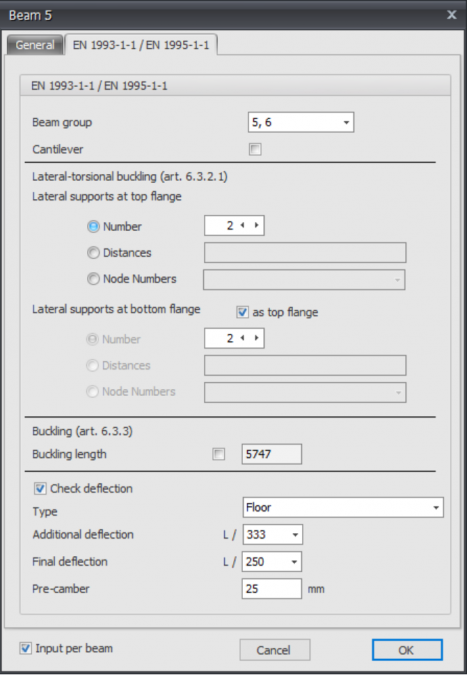
EN 1993-1-1 / EN 1995-1-1
Specifically and only for the check according to Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 respectively Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 data can be inserted.
Beam group
Specifically and only for the lateral-torsional buckling resistance check a beam group can be inserted here. XFrame2d automatically detects for which beams this qualifies. Only the beams which are connected by a fully fixed connection to this particular beam and have the same profile will be shown. You can select which beams should be taken into account. For this group you subsequently enter the length between the lateral restraints and the buckling length out of plane. Cantilever
Cantilever
Setting if the beam should be considered as a cantilever.
Lateral torsional buckling
Amount of lateral supports / distances between lateral supports
This is only relevant for the check of lateral torsional buckling. You can enter the lateral supports for the top and the bottom flange. There are 3 possibilities:
There are 3 possibilities:
1. Number: The amount of lateral supports. They are the extra (lateral supports) between the supports distributed over the length of the beam(group)
2. Distances: The lengths between the lateral restraints from the beginning of the beam (group). The syntax is length1 length2 amountxlenght3.. etc. For example 3000 3x2200 2800
3. Node numbers Selecting the node numbers which are in the beam group. Buckling length
Buckling length
The buckling length out of plane. According to the check by Eurocode 3: NEN-EN 1993-1-1 resp. Eurocode 5: NEN-EN 1995-1-1 this is based on a geometric non linear force distribution. This means that the buckling of the beams in the plane of the frameworks is provided implicitly. For every load combination the internal stability is determined iteratively.
However buckling out of the plane should be reviewed. Default the buckling lengths out of plane are taken equal to the beam length. In case this does not hold a different buckling length can be entered.
Check deflection
Setting if deflection has to be checked.
Type
This influences the requirement of additional deflection.
Additional deflection
Requirement of additional deflection.
Final deflection
Requirements of final deflection.
Pre-camber
The size of pre-camber in mm.